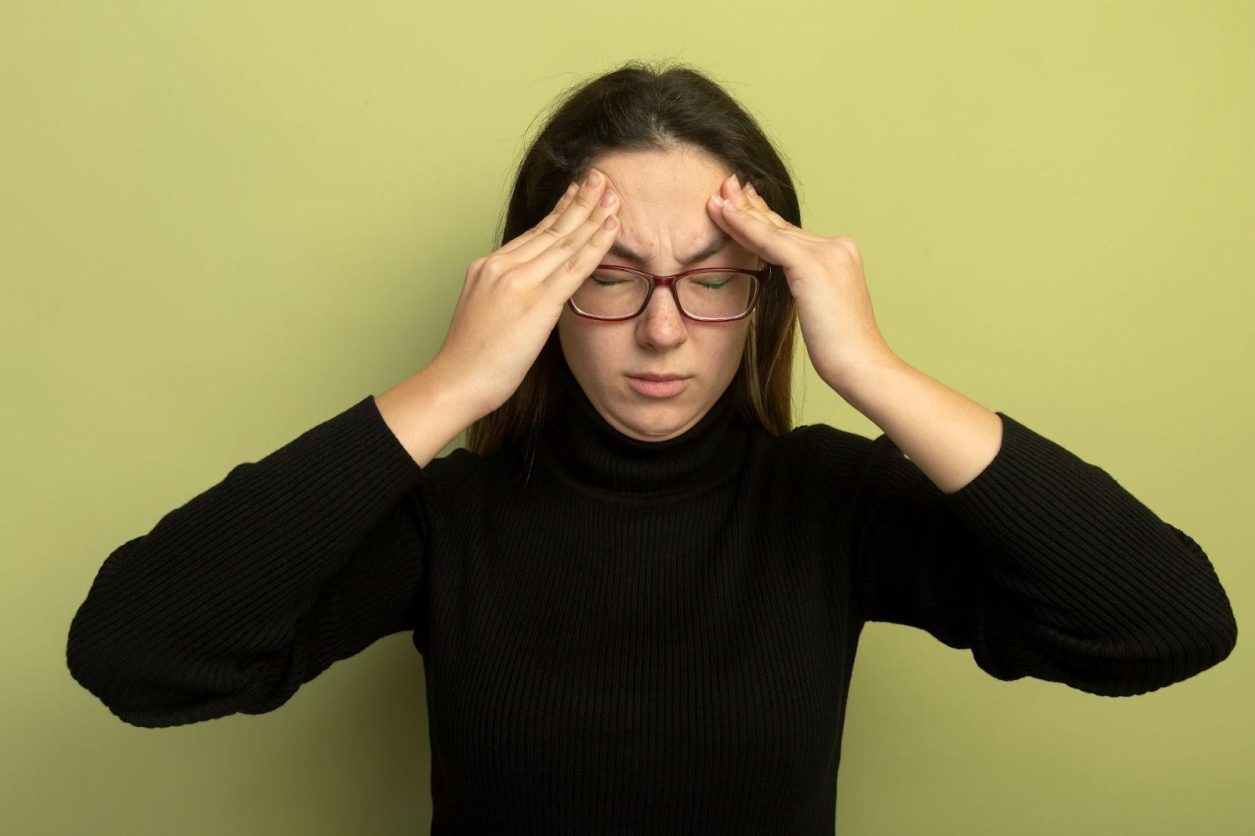
Headaches are a common issue that affects people of all ages. They can range from mild discomfort to intense, debilitating pain. Pain or pressure behind the eyes is a common symptom of headaches, which can impact daily life and make it difficult to carry out routine activities.
To effectively manage headache symptoms, it’s important to understand their causes and possible treatments. Understanding the underlying cause of your headache can help you take the necessary steps to find relief and prevent future headaches from occurring.
Causes of Headache, Pain, and Pressure Behind the Eyes
- Sinusitis: Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses, which are the cavities around the nose and eyes. When the sinuses become infected or inflamed, they can cause pressure or pain in the eyes and forehead. Nasal congestion, a runny nose, and facial pain often accompany this headache.
- Migraine: A migraine is a type of headache that affects many people. It is characterised by a throbbing or pulsing pain, often on one side of the head. In addition, migraines can cause other symptoms, such as light sensitivity, nausea, and visual disturbances.
- Eyestrain: Eye Strain occurs when the eyes are fatigued or strained, often from prolonged screen time or reading. This can cause a headache, pain or pressure behind the eyes. Headaches related to eyes or vision are usually mild and typically occur after working at near for sometime.
- Cluster Headache: A cluster headache is a type of headache that recurs in clusters and can cause pain or pressure behind the eyes. This headache is often severe and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as watering or redness in the eye.
Symptoms of Headache, Pain, and Pressure Behind the Eyes
- Pain or Pressure Behind the Eyes: One of the most common symptoms of headache, pain, and pressure behind the eyes is, as the name suggests, pain or pressure in this area. This pain or pressure can be mild or severe and impact daily life, making it difficult to carry out routine activities.
- Sinus Pressure or Pain: Sinusitis, as mentioned earlier, is an inflammation of the sinuses that can cause pressure or pain in the eyes and forehead. This headache is often accompanied by other symptoms such as nasal congestion, runny nose, and facial pain.
- Tension Headache: Tension headaches are the most common type of headache and can cause pain or pressure behind the eyes, as well as other symptoms such as tightness or pressure in the neck and shoulders.
Treatment Options for Headache, Pain, and Pressure Behind the Eyes
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and tension, which can contribute to headache symptoms.
- Cold or hot therapy: Applying a cold or hot compress to the affected area can help relieve headache pain and pressure behind the eyes.
- Light therapy: Exposure to bright light, either natural or artificial, can help alleviate symptoms of migraines and other types of headaches.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce stress, improve sleep, and alleviate headache symptoms.
- Healthy diet: Eating a healthy and balanced diet, including foods rich in magnesium and riboflavin, can help prevent headaches and reduce symptoms.
- Sleep: Sleeping and maintaining a regular sleep schedule can help prevent headaches and reduce symptoms.
- Medications specifically for migraines: If you have migraines, your doctor may prescribe medications designed to treat this type of headache. These may include triptans, which can help relieve the pain, or preventatives, which can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Behavioural therapy (stress management, relaxation techniques): Stress can trigger headaches, and managing stress through techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help alleviate headaches.
- Surgery for chronic sinusitis: In severe cases of chronic sinusitis, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure and pain in the eyes and forehead.
- Prescription eyegalsses or spectacles: If the headache is due to a vision defect like hypermetropia, astigmatism or presbyopia or other binocular vision issues like convergence, accommodation or muscular weakness of the entraocular muscles then precription eyeglasses will help treat as well as prevent the headaches.
Prevention of Headache, Pain, and Pressure Behind the Eyes
- Maintaining good eye hygiene (reducing screen time, regularly looking away from screens): Prolonged screen time can strain the eyes and trigger headache symptoms. Taking regular breaks and looking away from screens can help prevent eye strain and headaches.
- Reducing stress: Stress is a common trigger for headaches. Engaging in activities that help you manage stress, such as exercise, mindfulness, or hobbies, can help prevent headaches.
- Practising good sleep hygiene: Getting enough sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help prevent headaches.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve circulation, reduce stress, and improve overall physical and mental health, which can help prevent headaches.
- Regular Eye exam: Regular vision examinations with a qualified eyecare professional (ECP) will help identify presence of as well as cahnge in your eyegalss numbers that could be causing eye fatigue and headaches. Update the prescription in the eyegalsses each time there is even a slight cahnge.
- Eye exercises: Often times muscular weakenss causing problems in convergence and accommodation could be a problem. In such cases eye exercises can help aleviate the issues. EVen without any eye realted issues, simple eye relaxation exercises are helpful to prevent headaches caused by eye-fatigue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the causes and symptoms of headache, pain, and pressure behind the eyes is important for effectively managing these symptoms. Treatment options are available, from over-the-counter pain relievers to surgery and taking preventative measures such as maintaining good eye hygiene, reducing stress, and practising good sleep hygiene. Regular exercise can help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. If you experience persistent headaches, pain, or pressure behind the eyes, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Vision and eye examination are a great first play to begin eliminating causes for mild, dull headaches. If this exam is normal or if the headaches persist even after the appropriate spectacles and exercises, one may seek opinion of other specialists.